Indian Digital Currency | e-Rupee | (e₹) – Part 1
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced a new digital version of the Indian rupee called the e-Rupee (e₹). It is official money in electronic form created and supported by the RBI.
Unlike private cryptocurrencies that often change in value the e-Rupee stays stable and carries the same trust as regular cash. This digital currency aims to make payments safer and faster while keeping the value of money secure.
The RBI started testing the e-Rupee for both large financial transactions and everyday public use (like wholesale and Retail versions) in late 2022.
Also Read: PF Salary Limit Increased to 25000 Rupees; An EPFO Initiative, Direct benefits to Employees
Indian digital Currency

How would explain e-Rupee
The e-Rupee is a digital form of the Indian rupee created by the RBI – Reserve Bank of India . It holds the same value and legal status as paper money and can be exchanged equally for regular cash.
This digital currency is part of the RBI’s Central Bank Digital Currency called CBDC system.
Generally It’s distribution happens in two stages — first the RBI releases the digital tokens to commercial banks and then these banks make them available to the public through digital wallets.
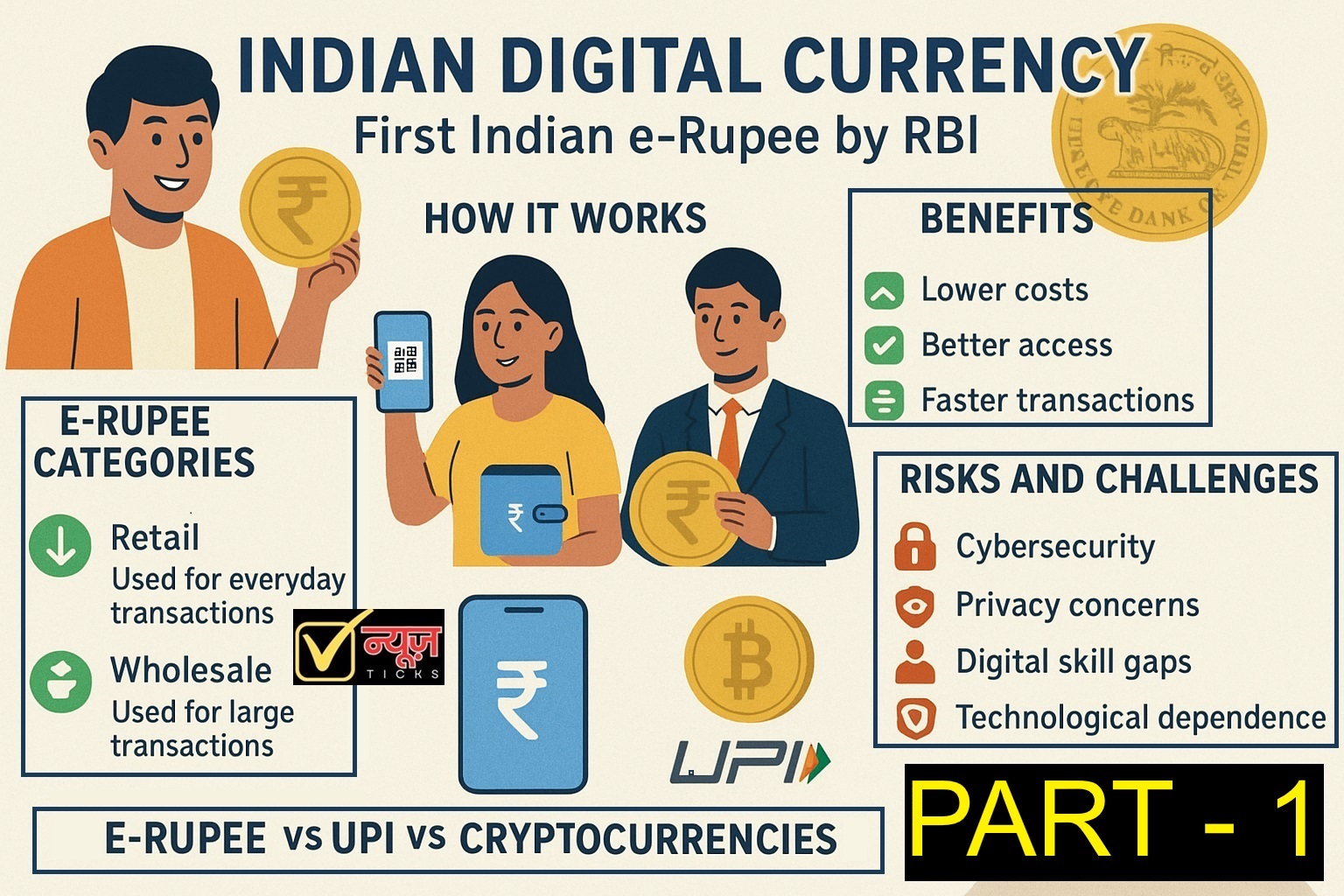
Indian digital Currency or e-Rupee Categories
The Reserve Bank of India has introduced two variants of the digital rupee for different uses.
(i). The Retail Digital Rupee (e₹-R): is meant for everyday transactions by individuals and businesses. It can be used for sending money between people or for making payments to shops and service providers.
(ii). Wholesale Digital Rupee (e₹-W): is designed for banks and financial institutions. It helps in handling large transactions and settling payments between banks especially in areas like government securities and financial markets.
How Indian Digital Currency or e-Rupee works
e-Rupee is based on advanced digital technology, designed to make money transfers faster, safer and more reliable in terms of technology, delivery, security and usage.
(i). Technology: It works on a system called Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) which is similar to blockchain. The wholesale version (e₹-W) uses a controlled or permissioned blockchain while the retail version uses a mix of technologies to handle large numbers of transactions smoothly.
(ii). Transactions: People can make payments using digital wallets offered by banks. Transactions can be completed by scanning a QR code or using other contactless methods.
(iii). Distribution: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) creates the digital money and gives it to banks. These banks then make it available for customers to store the e-Rupee in their digital wallets and use it for payments for both online and offline Transactions.
(iv). Privacy: For smaller payments, the system is designed to offer privacy similar to cash transactions. However, larger payments are monitored under anti-money laundering and anti-terror financing laws to ensure safety and transparency.
(v). Offline Use: The RBI is working on features that allow the e-Rupee to be used even without an internet connection. This will help people in rural or remote areas where online access is limited.
(vi). Programmable Use: The e-Rupee can also be set up for specific purposes. For instance, government subsidies or loans can be programmed so that the money is used only for its intended goal.
Also Read: 8th Pay Commission 2026: Good Relief for Central government Employees, Full Details Explored
Benefits of e-Rupee

(i). Lower costs: The digital rupee helps cut down the heavy expenses involved in printing, moving and storing paper money.
(ii). Better access: With features like offline usage and digital wallet, e-Rupee makes it easier for people in remote or rural areas especially those who do not have bank accounts, to participate in the financial system.
(iii). Faster transactions: Since the e-Rupee is directly backed by the Reserve Bank of India therefore payments are completed and final in jiffy. Even it help in avoiding delays that often happen in regular bank transfers.
(iv). More safety and clarity: The use of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) reduces the chances of fake currency and adds more transparency which helps in preventing illegal money activities.
(v). Support for innovation: The e-Rupee can become a strong base for new ideas in digital payments and can also make cross border money transfers quicker and more efficient.
e-Rupee vs UPI vs Crypto Currency
| Feature | e-Rupee by CBDC | UPI – Based Digital Money | Cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin, Ethereum etc.) |
| Issuer | Reserve Bank of India (RBI) | Commercial banks and payment providers | Decentralized, no central authority |
| Backing | Fully sovereign-backed by the RBI | Represents a claim on existing bank deposits | No sovereign or asset backing; price is speculative |
| Legal Status | Legal tender | A payment interface for transferring existing money | Not a legal tender |
| Settlement | Instant and final settlement on the RBI’s ledger | Transfers occur between bank accounts which routed through banks and NPCI | Peer-to-peer settlement but network confirmation can vary |
| Offline use | Designed with offline capability for use without an internet connection | Generally, It requires a live internet connection | Requires a live internet connection in any situation |
| Stability | Stable with a 1:1 fixed value with the physical rupee | Stable but tied to the value of the Indian rupee | Highly volatile and speculative |
The Pilot Banks
Currently, 15 Pilot banks are offering Central Bank Digital Currency – CBDC wallets.
| Pilot Banks | Name of the App available on Android and Apple |
| SBI | eRupee by SBI |
| ICICI Bank | Digital Rupee by ICICI Bank |
| IDFC First Bank | IDFC First Bank Digital Rupee |
| YES BANK | Yes Bank Digital Rupee |
| HDFC Bank | HDFC Bank Digital Rupee |
| Union Bank of India | Digital Rupee by UBI |
| Bank of Baroda | Bank of Baroda Digital Rupee |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | Digital Rupee by Kotak Bank |
| Canara Bank | Canara Digital Rupee |
| Axis Bank | Axis Mobile Digital Rupee |
| IndusInd Bank | Digital Rupee by IndusInd Bank |
| PNB | PNB Digital Rupee |
| Federal Bank | Federal Bank Digital Rupee |
| Karnataka Bank | Karnataka Bank Digital Rupee |
| Indian Bank | Indian Bank Digital Rupee |
| IDBI Bank | IDBI eRupee |
| Bank of India | Bank of India Digital eRupee |

Risks and Challenges of the e-Rupee
(i). Cybersecurity: Being fully digital the e-Rupee system can face risks like hacking, online scams or sometimes cyberattacks too. Strong protection measures are needed to keep the system safe and reliable.
(ii). Privacy issues: Since digital transactions can be tracked especially for large amounts so there are concerns about how much personal financial information remains private. The Reserve Bank of India aims or needed to create a balance between privacy and related regulatory oversight.
(iii). Digital skills and Access: Successful use of the e-Rupee depends on good internet connectivity and related basic digital knowledge which can be limited in certain regions of the country that needs improvements.
(iv). Dependence on technology: This system is completely based on technology so any technical glitch like power failure or network problem or major disasters can affect the transactions and daily operations or even the system itself.
(v). Market competition: The e-Rupee will need to find its place alongside already popular digital payment methods such as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) which many people and businesses currently prefer for their daily transactions.
More About : Indian digital Currency
To be continued…
Discover more from Newz Ticks
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.